Introduction
Ellipse ဆိုသည်မှာ ပြင်ညီတစ်ခုပေါ်ရှိ ဘဲဥပုံသဏ္ဌာန် ပတ်လမ်းကြောင်းဟု အလွယ်ပြောနိုင်သည်။ Solar System (နေအဖွဲ့အစည်း) အတွင်းရှိ ဂြိုဟ်ပတ်လမ်းကြောင်းများသည် ellipse ပုံ သဏ္ဌာန်နှင့် အနီးစပ်ဆုံး တူညီသည်။ လက်တွေ့နယ်ပယ်တွင် Ellipse ကိုအလှဆင်ခြင်းနှင့် ဒီဇိုင်းပြုလုပ်ရန်အတွက် ဗိသုကာတွင် ကျယ်ပြန့်စွာအသုံးပြုသည်။ Whispering Chambers ဟုခေါ်သော အချို့သော အဆောက်အအုံများကို elliptical domes (ဘဲဥပုံအမိုးခုံး) ဖြင့်တည်ဆောက်လေ့ရှိသည်။ အောက်ပါပုံကို ကြည့်ပါ။ Ellipse ၏ ဂုဏ်သတ္တိကြောင့် $F_1$ ၌ ရပ်နေသော လူ၏ ပြောစကားများ သာမန်ဖြင့် မကြားနိုင်သည့် အကွာအဝေးတွင်ရှိသော $F_2$ မှလူက အလွယ်တကူ ကြားနိုင်သည်။
Definition
An ellipse is the set of all points, P, in a plane the sum of whose distances from two fixed points, $F_1$ and $F_2$, is constant.These two fixed points are called the foci (plural of focus). The midpoint of the segment connecting the foci is the center of the ellipse.
- အမှတ်သေ (မရွေ့လျားသောအမှတ်) နှစ်ခု $F_1$ မှ $F_2$ အကွာအဝေးနှစ်ခု ပေါင်းခြင်းသည် ကိန်းသေ ($PF_1+ PF_2$ = constant) ဖြစ်နေသော အမှတ်အားလုံးပါဝင်သည့်အစု ($P$ အမှတ်၏ ရွေ့လျားရာ လမ်းကြောင်း) ကို ellipse ဟုခေါ်သည်။
- $F_1$ နှင့် $F_2$ ကို ellipse ၏ ဆုံချက်များ (foci) ဟုခေါ်သည်။
- $F_1$ နှင့် $F_2$ ၏ အလယ်မှတ်ကို ellipse ၏ center ဟုခေါ်သည်။
Important Terms
- Foci are the distinct fixed points in the plane such that the sum of the distances from each point on an ellipse is constant.
Foci (ဆုံချက်များ) ဆိုသည်မှာ မရွေ့လျားနိုင်သော အမှတ်သေနှစ်ခု ဖြစ်ပြီး၊ ellipse ပေါ်ရှိအမှတ်တစ်ခုမှ ထိုအမှတ်နှစ်ခုကို ဆက်သွယ်ထားသော မျဉ်းပြတ်များ၏ အလျားများပေါင်းခြင်းသည် ကိန်းသေဖြစ်သည်။ - Vertices are the points of intersection of an ellipse and the line through its foci.
Focus နှစ်ခုဖြတ်သွားသော မျဉ်းနှင့် ellipse တို့ ဖြတ်သောအမှတ်များ ကို Vertices ဟုခေါ်သည်။ - Major axis is the chord connecting the vertices of an ellipse.
Vertices နှစ်ခုကိုဆက်သွယ်ထားသော မျဉ်းကို major axis ဟုခေါ်သည်။ - Centre is the midpoint of the segment connecting the foci of an ellipse.
foci နှစ်ခုကိုဆက်ထားသော မျဉ်းပြတ်၏ အလယ်မှတ်ကို centre ဟုခေါ်သည်။ - Minor axis is the chord perpendicular to the major axis at the center of an ellipse.
major axis ကို centre ၌ ထောင့်မှတ်ကျသော မျဉ်းကို minor axis ဟုခေါ်သည်။ - Co-Vertices are the points of intersection of an ellipse and its minor axis.
minor axis နှင့် ellipse တို့ ဖြတ်သောအမှတ်များကို co-vertices ဟုခေါ်သည်။ - Length of major axis $ = 2a$
- Length of minor axis $ = 2b$
$PF_1+PF_2=\text{constant}$
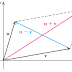
Ellipse ပုံတစ်ခုကို အောက်ဖေါ်ပြပါပုံအတိုင်း လက်တွေ့ ရေးဆွဲနိုင်ပါသည်။
ပုံတွင်မြင်တွေ့ရသည့်အတိုင်း $PF_1$ နှင့် $PF_2$ အလျားနှစ်ခုပေါင်းခြင်းသည် တင်း၍ဆွဲထားသော ကြိုး၏ အလျားပင် ဖြစ်သည်။ $P$ ဆိုသည်မှာ ခဲတံထောက်ထားသော နေရာကို ဆိုလိုသည်။ ခဲတံမည်သည့်နေရာတွင် ရှိပါစေ $PF_1+ PF_2$ = length of string ဖြစ်သောကြောင့် constant ဖြစ်ကြောင်း အလွယ်သိနိုင်သည်။
$PF_1+ PF_2 = 2a$ ဖြစ်ကြောင်း သက်သေပြပါမည်။ $P$ သည် မည်သည့်နေရာတွင် ရှိသည်ဖြစ်စေ $PF_1+ PF_2$ သည် ကိန်းသေဖြစ်ကြောင်း သိရှိခဲ့ပြီး ဖြစ်သည်။ ထို့ကြောင့် သက်သေပြချက်လွယ်ကူစေရန် $P$ သည် Ellipse ၏ vertex နေရာ၌ရှိသည့် အခြေအနေဖြင့် သက်သေပြပါမည်။
Vertex နေရာတွင် $P$ ရှိနေသည့်အခါ $PF_1 = a+c$ and $PF_2=a-c$ ဖြစ်မည်။
ထို့ကြောင့် $PF_1+ PF_2 = a+c + a-c =2a$ ဖြစ်ကြောင်း အလွယ်တကူသိနိုင်သည်။
$a, b$ နှင့် $c$ တို့၏ ဆက်သွယ်ချက်ကို ရှာရန် အောက်ပါအခြေအနေဖြင့် စဉ်းစားပါမည်။
သတ်မှတ်ထားသော ellipse တစ်ခုအတွက် $P$ သည် မည်သည့်နေရာတွင် ရှိသည်ဖြစ်စေ $a, b, c$ တို့၏ တန်ဖိုးပြောင်းလဲခြင်း မရှိပါ။
ထို့ကြောင့် ဆက်သွယ်ချက်ကို ရှာရန် လွယ်ကူစေဖို့ $P$ သည် Ellipse ၏ co-vertex နေရာ၌ရှိသည့် အခြေအနေဖြင့် တင်ပြပါမည်။
Co-Vertex နေရာတွင် $P$ ရှိနေသည့်အခါ $PF_1 = PF_2 = a$ ဖြစ်မည်။ Pythagoras' Theorem အရ $a^2 = b^2 + c^2$ ဖြစ်ပါမည်။
Ellipse with Centre at $(0,0)$
Curve တစ်ခု လမ်းကြောင်းပေါ်ရှိ $(x,y)$ အမှတ်များ၏ အစုအဝေးကို ၎င်း curve ၏ equation ဟုခေါ်သည်။ curve လမ်းကြောင်းပေါ်ရှိ မည်သည့် အမှတ် $(x, y)$ မဆို curve equation ကို ပြေလည်စေသည်။ တနည်းဆိုသော် ပေးထားသော equation ကို ပြေလည်စေသော အမှတ်တစ်ခု ရွေ့လျားရာ လမ်းကြောင်း (locus) ကို Curve ဟုခေါ်သည်။
ဆက်လက်၍ centre က $(0,0)$ ရှိသော ellipse တစ်ခု၏ standard equation ကို တင်ပြပါမည်။
| Center : $(0,0)$ Verteices : $(-a,0)$ and $(a,0)$ Co-Vertices : $(-b,0)$ and $(b,0)$ Foci : $(-c,0)$ and $(c,0)$ Lenght of major axis = $2a$ Lenght of minor axis = $2b$ $PF_1=\sqrt{(x+c)^2+y^2}$ $PF_2=\sqrt{(x-c)^2+y^2}$ $\begin{array}{l}\ \ \text{For any point }P(x,y)\text{ on the ellipse,}\\\\\ \ P{{F}_{1}}+P{{F}_{2}}=2a\\\\\therefore \ \sqrt{{{{{(x+c)}}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}}}+\sqrt{{{{{(x-c)}}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}}}=2a\\\\\ \ \sqrt{{{{{(x+c)}}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}}}=2a-\sqrt{{{{{(x-c)}}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}}}\\\\\ \ \ \text{Squaring both sides,}\\\\\ \ \ {{(x+c)}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=4{{a}^{2}}-4a\sqrt{{{{{(x-c)}}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}}}+{{(x-c)}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}\\\\\ \ \ {{(x-c)}^{2}}-\ {{(x+c)}^{2}}+4{{a}^{2}}=4a\sqrt{{{{{(x-c)}}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}}}\\\\\ \ \ (x-c+x+c)\ (x-c-x-c)+4{{a}^{2}}=4a\sqrt{{{{{(x-c)}}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}}}\\\\\ \ \ (2x)\ (-2c)+4{{a}^{2}}=4a\sqrt{{{{{(x-c)}}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}}}\\\\\ \ \ 4{{a}^{2}}-4cx=4a\sqrt{{{{{(x-c)}}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}}}\\\\\ \ \ 4{{a}^{2}}-4cx=4a\sqrt{{{{{(x-c)}}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}}}\\\\\ \ \ {{a}^{2}}-cx=a\sqrt{{{{{(x-c)}}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}}}\\\\\ \ \ \text{Squaring both sides,}\\\\\ \ \ {{a}^{4}}-2{{a}^{2}}cx+{{c}^{2}}{{x}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}{{(x-c)}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}{{y}^{2}}\\\\\ \ \ {{a}^{4}}-2{{a}^{2}}cx+{{c}^{2}}{{x}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}({{x}^{2}}-2cx+{{c}^{2}})+{{a}^{2}}{{y}^{2}}\\\\\ \ \ {{a}^{4}}-2{{a}^{2}}cx+{{c}^{2}}{{x}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}{{x}^{2}}-2{{a}^{2}}cx+{{a}^{2}}{{c}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}{{y}^{2}}\\\\\ \ \ {{a}^{4}}+{{c}^{2}}{{x}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}{{x}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}{{c}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}{{y}^{2}}\\\\\ \ \ ({{a}^{2}}-{{c}^{2}}){{x}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}{{y}^{2}}={{a}^{4}}-{{a}^{2}}{{c}^{2}}\\\\\ \ \ \text{Since}\ {{a}^{2}}={{b}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}},{{c}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}}\\\\\ \ \ ({{a}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}){{x}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}{{y}^{2}}={{a}^{4}}-{{a}^{2}}({{a}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}})\\\\\ \ \ {{b}^{2}}{{x}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}{{y}^{2}}={{a}^{4}}-{{a}^{4}}+{{a}^{2}}{{b}^{2}}\\\\\ \ \ {{b}^{2}}{{x}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}{{y}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}{{b}^{2}}\\\\\ \ \ \text{Dividing both sides with }{{a}^{2}}{{b}^{2}}\text{,}\\\\\ \ \ \displaystyle\frac{{{{b}^{2}}{{x}^{2}}}}{{{{a}^{2}}{{b}^{2}}}}+\displaystyle\frac{{{{a}^{2}}{{y}^{2}}}}{{{{a}^{2}}{{b}^{2}}}}=\displaystyle\frac{{{{a}^{2}}{{b}^{2}}}}{{{{a}^{2}}{{b}^{2}}}}\\\\\ \ \ \displaystyle\frac{{{{x}^{2}}}}{{{{a}^{2}}}}+\displaystyle\frac{{{{y}^{2}}}}{{{{b}^{2}}}}=1\end{array}$ |
|---|
အထက်ဖော်ပြပါ equation တွင် major axis သည် horizontal ဖြစ်သည်။ အကယ်၍ major axis သည် vertical ဖြစ်လျှင် ellipse ၏ equation မှာ $\displaystyle\frac{x^{2}}{b^{2}}+\frac{y^{2}}{a^{2}}=1$ ဖြစ်သွားပါမည်။
















0 Reviews:
Post a Comment