Introduction
ထိပ်ချင်းဆိုင်ထားသော ကတော့ချွန် (Cone) နှစ်ခုကို ပြင်ညီတစ်ခုနှင့် ပိုင်းဖြတ်လိုက်သောအခါ ရရှိလာသည့် အစိပ်အပိုင်းများကို Conic Sections ဟုခေါ်သည်။ ပိုင်းဖြတ်လိုက်သော ပြင်ညီ၏ တည်နေပုံ (ထောင့်အနေအထား) ကို လိုက်၍ Conic Sections များကို
- Circle
- Ellipse
- Parabola
- Hyperbola
- Intersecting Lines
Parabola
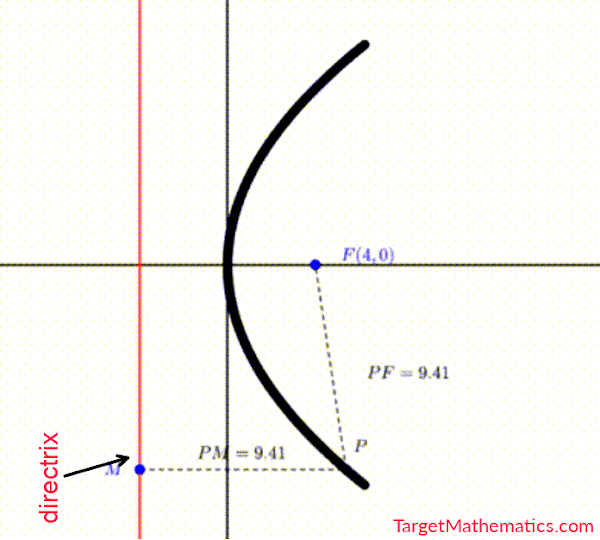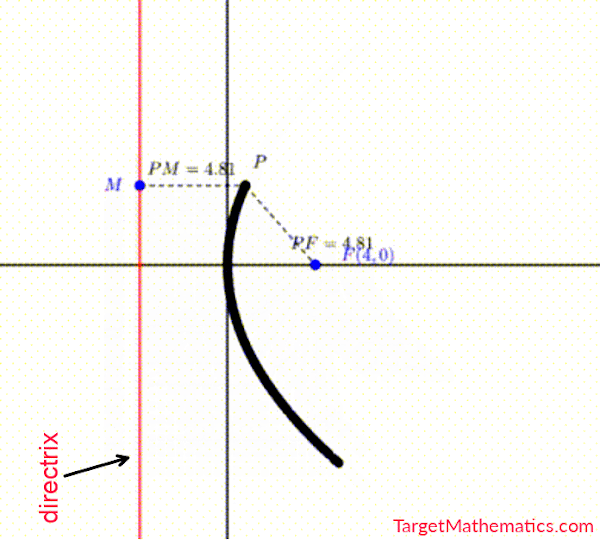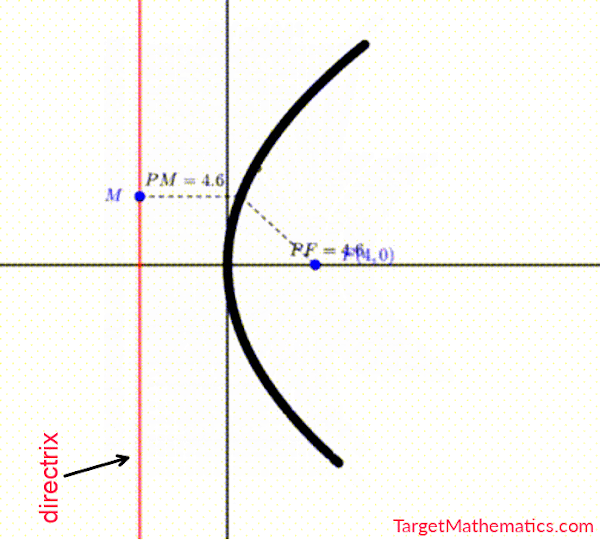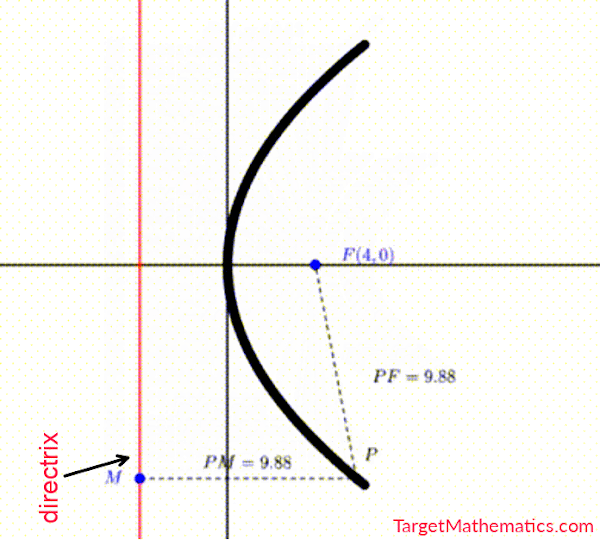
- ပေးထားသော applet ရှိ အမှတ် $P$ ကို ပွတ်ဆွဲပြီး ရွှေ့ကြည့်ပါ။
- အမှတ် $P$ သည် အမှတ်သေ (မရွေ့လျားသော အမှတ်) $F$ နှင့် မျဉ်းသေ (မရွေ့လျားသော မျဉ်း) $L$ မှ အမြဲတူညီစွာ ကွားဝေးနေသည်ကို တွေ့ရပါမည်။
- အမှတ်ရှင် (ရွေ့လျားနိုင်သော အမှတ်) $P$ ကို နေရာလိုက်ပြီး $P_1, P_2, P_3, \text{etc}.$ စသဖြင့် အမည်သတ်မှတ်သည် ဆိုပါစို့။ တည်နေရာမတူသော $P$ အမှတ်များ၏ အစုအဝေးကို မျဉ်းကွေး (Curve) အဖြစ် တွေ့မြင်ရမည် ဖြစ်ပြီး၊ အဆိုပါ curve ကို Parabola ဟုခေါ်သည်။
- အမှတ်သေ (fixed point) $F$ ကို Focus ဟုခေါ်ပြီး၊ မျဉ်းသေ (fixed line) $L$ ကို Directrix ဟုခေါ်သည်။
- ထို့ကြောင့် Parabola ဆိုသည်မှာ Focus နှင့် Directrix တို့မှ တူညီစွာဝေးကွာသည့် အမှတ်များပါဝင်သော အစုဟု အဓိပ္ပါယ်သတ်မှတ်နိုင်ပါသည်။
| Definitions - Parabola A set that consists of all the points in a plane equidistant from a given fixed point and a given fixed line in the plane is a parabola. The fixed point is the focus of the parabola. The fixed line is the directrix. |
|---|
Focus သည် $\text{positive}\ x-\text{axis}$ ပေါ်ရှိ အမှတ်တစ်ခု $(0,p)$ ဖြစ်သည်ဟု ယူဆမည်။ Directrix သည် $(0,-p)$ ကို ဖြတ်သွားသော horizontal line (ရေပြင်ညီမျဉ်း) ဖြစ်သည်ဟု ယူဆမည်။
ထိုအခါ parabola သည် $(0,p)$ နှင့် $(0,-p)$ တို့၏ အလယ်မှတ်ဖြစ်သော $(0,0)$ ကို ဖြတ်သွားမည်။ ၎င်းကို parabola ၏ vertex ဟုလည်း ခေါ်သည်။ Vertex နှင့် Focus သည် တူညီသော ထောင်လိုက် သို့မဟုတ် ရေပြင်ညီ မျဉ်းတစ်ကြောင်းတည်း ပေါ်တွင်သာ ရှိသည်။ Vertex နှင့် Focus ကြားအကွာအဝေး |p| ကို parabola ၏ focal lenght ဟုခေါ်သည်။ Parabola ၏ vertex ကို ကန့်လန့်ဖြတ်ပြီး Parabola ကို ခေါက်ချိုးညီထက်ဝက်ပိုင်း သွားသော $y-\text{axis}$ ကို Axis of Symmetry (ခေါက်ချိုးညီ ဝင်ရိုး) ဟု ခေါ်သည်။
အမှတ် $P$ မှ directrix ပေါ်သို့ ထောင့်မတ်ကျသော မျဉ်းသည် directrix ကို $Q$ ၌ ဖြတ်သည်ဆိုပါစို့။ Parabola ၏ အဓိပ္ပာယ်သတ်မှတ်ချက်အရ $PF=PQ$ အမြဲဖြစ်ပါမည်။ ထို့ကြောင့် PF:PQ = 1 ဖြစ်လျှင် parabola ဟုခေါ်သည်။ အဆိုပါ PF နှင့် PQ အချိုးကို conic section တစ်ခု၏ eccentricity ($e$) ဟု သတ်မှတ်သည်။
Distance Formula အရ ...
$\begin{array}{l} P F=\sqrt{(x-0)^{2}+(y-p)^{2}}=\sqrt{x^{2}+(y-p)^{2}} \\\\ P Q=\sqrt{(x-x)^{2}+(y+p)^{2}}=\sqrt{(y+p)^{2}} \\\\ \therefore \sqrt{x^{2}+(y-p)^{2}}=\sqrt{(y+p)^{2}} \\\\ x^{2}+(y-p)^{2}=(y+p)^{2} \\\\ x^{2}=(y+p)^{2}-(y-p)^{2} \\\\ x^{2}=(y+p+y-p)(y+p-y+p) \\\\ x^{2}=(2 y)(2 p) \\\\ x^{2}=4 p y \text { or } y=\displaystyle\frac{x^{2}}{4 p} \end{array}$
ထို့ကြောင့် Focus က $(0,p)$ ၌ ရှိပြီး directrix : $y=-p$ ဖြစ်လျှင် parabola ၏ equation ကို $x^{2}=4 p y \text { or } y=\displaystyle\frac{x^{2}}{4 p}$ ဟု အလွယ်တကူ ပြောနိုင်သည်။ Parabola Shape မှာ Opens Up ဖြစ်မည်။
အကယ်၍ Focus က $(0,-p)$ ၌ ရှိပြီး directrix : $y=p$ ဖြစ်လျှင် parabola ၏ equation မှာ $x^{2}=-4 p y \text { or } y=-\displaystyle\frac{x^{2}}{4 p}$ ဖြစ်ပြီး Opens Down Parabola ကို ရရှိမည် ဖြစ်သည်။ အောက်ပါ applet မှာ အမှတ် $P$ ကို ပွတ်ဆွဲကြည့်ပါ။
အကယ်၍ Focus က $(p,0)$ ၌ ရှိပြီး directrix : $x=-p$ ဖြစ်လျှင် parabola ၏ equation မှာ $y^{2}=4px \text { or } x=\displaystyle\frac{y^{2}}{4 p}$ ဖြစ်ပြီး Opens Right Parabola ကို ရရှိမည် ဖြစ်သည်။အောက်ပါ applet မှာ အမှတ် $P$ ကို ပွတ်ဆွဲကြည့်ပါ။
ထိုနည်းတူစွာ Focus က $(-p,0)$ ၌ ရှိပြီး directrix : $x=p$ ဖြစ်လျှင် parabola ၏ equation မှာ $y^{2}=-4px \text { or } x=-\displaystyle\frac{y^{2}}{4 p}$ ဖြစ်ပြီး Opens Left Parabola ကို ရရှိမည် ဖြစ်သည်။ ဖော်ပြပါ parabola ပုံသဏ္ဌာန် လေးမျိုးကို အောက်ပါအတိုင်းမှတ်သားနိုင်ပါသည်။
Standard Equations
Standard-form equations for parabolas with vertices at the origin (p > 0)
| Equation | Focus | Directrix | Axis | Opens |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| $x^{2}=4 p y$ | $(0, p)$ | $y=-p$ | $y \text { -axis }$ | UP |
| $x^{2}=-4 p y$ | $(0, -p)$ | $y=p$ | $y \text { -axis }$ | DOWN |
| $y^{2}=4 p x$ | $(p, 0)$ | $x=-p$ | $x \text { -axis }$ | RIGHT |
| $y^{2}=-4 p x$ | $(-p, 0)$ | $x=p$ | $x \text { -axis }$ | LEFT |
Terms of Parabola
Important Terms to Know
|
|---|
Worked Examples
| Example (1) Find the equation of the parabola with focus at (0, 4) and directrix the line y=-4. Solution Focus = (0,4), directrix : y= -4 Since the focus is on the positive y-axis at (0, 4) and the directrix is a horizontal line y=-4, the vertex of the parabola is (0,0). The equation of the parabola is of the form $x^2=4py$ where $p=4$. $\therefore \ \ x^2=4(4)y\ \ \ \text{or}\ \ \ y=\displaystyle\frac{x^2}{16}$ Example (2) Find the focus and directrix of the parabola $y^2= 10x$. Solution Parabola: $y^2= 10x$. Comparing with $y^2= 4px$, $\begin{array}{l} 4p=10\\\\ p=\displaystyle\frac{10}{4}=\displaystyle\frac{5}{2}\\\\ \therefore \ \ \ \text{focus}= (p,0)= \displaystyle \left( {\frac{5}{2},0} \right)\\\\ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \text{directrix}: x=-p \Rightarrow x= -\displaystyle\frac{5}{2} \end{array}$ Example (3) Find the equation of a parabola whose vertex is at (0, 0). If the axis of symmetry of the parabola is the $x$-axis and the point $\displaystyle \left( {-\frac{1}{2},2} \right)$ lies on the graph. Find its focus and directrix, and graph the equation. Solution vertex = (0,0) axis of symmetry = $x-\text{axis}$ point on the graph = $ \left( {-\displaystyle\frac{1}{2},2} \right)\Rightarrow 2^{\text{nd}}\ \text{quadrant}$ $\therefore$ The parabola opens to the left and its equation is of the form $y^2=-4px$ Since $ \left( {-\displaystyle\frac{1}{2},2} \right)$ lies on parabola, ${2}^2=-4p \left( {-\displaystyle\frac{1}{2},2} \right)$ $\therefore\ \ p=2$ $\therefore$ The equation of parabola : $y^2=-4(2)x\Rightarrow y^2=-8x$ $ \ \ \ \ \ \ \text{focus} = (-p,0) = (-2,0)$ $ \ \ \ \ \ \ \text{directrix} : x = p\Rightarrow x =2 $ $ \displaystyle \begin{array}{l}\text{When}\ x=-2,\ {{y}^{2}}=-8(-2)=16\\\\ \therefore \ \ y=\pm 4\end{array}$ Hence the parabola passes through the points $(-2,4)$, $\displaystyle \left( {-\frac{1}{2},2} \right)$, $(0,0)$ and $(-2,-4)$. |
|---|
Exercises
| Find the focus and directrix of each of the foloowing parabola equations and sketch the graph. $\begin{array}{ll} (1) & y^{2}=12 x\\\\ (2) & x^{2}=6 y\\\\ (3) & x^{2}=-8 y\\\\ (4) & y^{2}=-2 x\\\\ (5) & y=4 x^{2}\\\\ (6) & y=-8 x^{2}\\\\ (7) & x=-3 y^{2}\\\\ (8) & x=2 y^{2} \end{array}$ |
|---|












0 Reviews:
Post a Comment